Pump modelling
As liquid can be assumed incompressible, pump calculations are simpler compared to compressor calculations. The pumped fluid can be characterized with its density, and no fluid calculations are necessary.
The power demand of a pump is calculated as
Here, the relationship between head and pressures is given by
where and are the pump suction and discharge pressures, respectively, and is the gravitational constant.
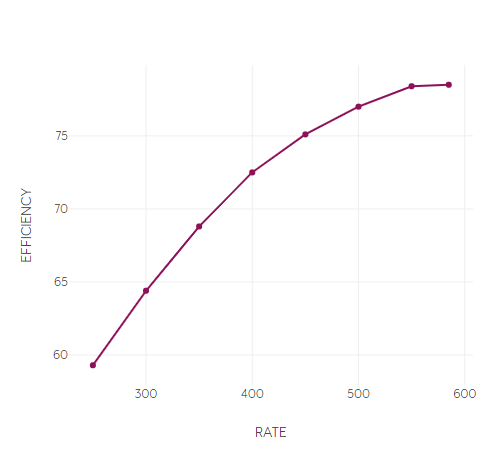
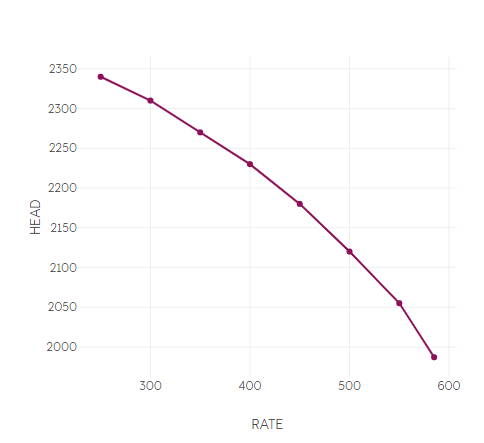
eCalc uses the pump chart to relate liquid flow, head and efficiency for the pump, as well as defining the operational envelope for the pump.
For single speed pumps, eCalc does extrapolations corresponding to minflow (liquid recirculation) and choking to keep the pump operation within the operational envelope.